Scattering of water waves by arrays of identical bodies
| Leadership: | Prof. Dr. Malte Peter |
| Processor: | |
| Project partner: |
M. H. Meylan, University of Auckland, Neuseeland C. M. Linton, Loughborough University, Großbritannien |
| Time period: | since 01.03.2004 |
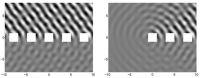
 Scattering of water waves by floating or submerged bodies in the water is of great practical importance, e.g. for the construction of structures in the ocean (oil rigs, wind mills, etc.) and in climate research (scattering by fields of ice floes).
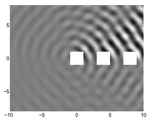
Scattering of water waves by floating or submerged bodies in the water is of great practical importance, e.g. for the construction of structures in the ocean (oil rigs, wind mills, etc.) and in climate research (scattering by fields of ice floes).Many technical structures (antennas, offshore platforms, etc.) consist of repeating elements with equal distances. In many applications, it is reasonable to replace the complex multi-body scattering problem by one in which the elements are assembled in an infinite array, i.e. the bodies are assembled along a straight line. If the incoming waves are also periodic, the resulting scattering problem is much simpler owing to the periodicity. In this case, the problem can be analytically reduced to one for a single element of the array. Many properties of the finite array can be studied using the substitute problem, e.g. scattering angles, certain resonances, etc.
Edge effect, i.e. properties determining the behaviour close to the beginning or the end of the finite array cannot be studied using the infinite array. For this purpose, it is possible to approximate the problem by one in which the elements are assembled periodically along a straight line extending to infinity in only one direction, the so-called semi-infinite array. This problem is much more difficult analytically and much more feasible numerically than the infinite array. However, the solution to the infinite-array problem can be used to design efficient numerical solution methods for the semi-infinite array. Moreover, it is possible to study special resonances, so-called Rayleigh–Bloch waves (also called surface waves or guided waves), which propagate along the array, and whose amplitude decays exponentially away from the array.